Understanding Structural Steel Construction
What is Structural Steel Construction?
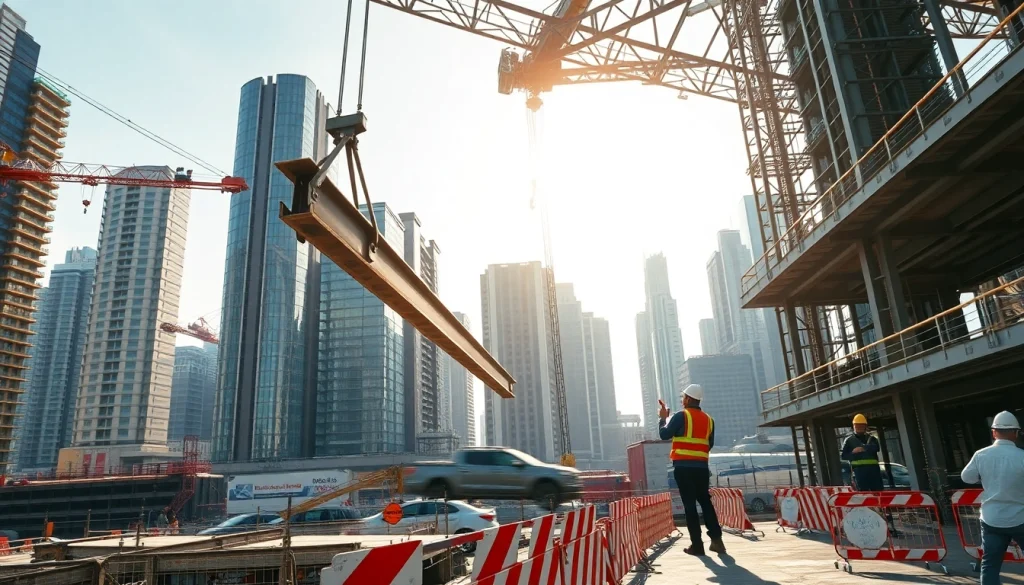
Structural steel construction refers to the method of building structures, such as bridges, skyscrapers, and industrial facilities, through the utilization of steel framing elements. This approach employs various steel shapes and sections that are fabricated and assembled to create a robust framework capable of supporting a building’s loads. The process begins with the design phase, where structural engineers specify material grades, dimensions, and configurations tailored to ensure structural integrity and safety. Steel is chosen due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, which enables it to carry substantial loads while maintaining lighter overall building weight. The versatility of structural steel construction makes it not only a practical choice but also allows for various architectural designs that might not be achievable using traditional materials like concrete or wood.
Benefits of Structural Steel Construction
Structural steel construction offers numerous advantages that contribute to its popularity among builders and designers:
- Durability: Steel is resistant to many environmental factors, including pests, rot, and fire, making it a long-lasting option for construction.
- Flexibility in Design: The material can be molded into various shapes and sizes, allowing architects to explore innovative designs while adhering to safety standards.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in steel may be higher than alternative materials, its longevity, reduced maintenance costs, and efficiency in construction can lead to lower overall expenses.
- Speed of Construction: Steel components can be pre-fabricated in a controlled environment, enabling faster assembly on-site, which minimizes labor costs and accelerates project timelines.
- Recyclability: Steel is highly recyclable, which supports sustainable construction practices and minimizes environmental impacts.
Common Applications of Structural Steel Construction
Structural steel construction finds its application across a wide range of projects:
- High-Rise Buildings: Steel’s strength allows for the construction of monumental skyscrapers that can reach impressive heights while maintaining safety and stability.
- Bridges: The use of steel in bridge construction provides the necessary support for heavy traffic loads and spans, offering long lifecycle benefits.
- Industrial Structures: Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants often utilize steel due to its ability to support large open spaces and heavy machinery.
- Arenas and Stadiums: Steel framing accommodates large roof structures and complex geometrical shapes required in sports facilities.
- Residential Buildings: Steel is becoming increasingly popular in residential construction for its strength, durability, and aesthetic potential.
Design Considerations for Structural Steel Construction
Load-Bearing Requirements
In structural steel construction, understanding load-bearing requirements is critical. Loads can be categorized into several types: dead loads, live loads, environmental loads, and dynamic loads. Dead loads are the permanent static forces acting on a structure, including the weight of structural elements themselves. Live loads, on the other hand, vary with occupancy and use, such as people and furniture in a building. Environmental loads encompass wind, seismic, and snow loads, while dynamic loads represent forces that occur during use, such as vibration from machinery. Structural engineers meticulously calculate these loads to ensure the steel framework is designed to bear them safely without deformation or failure, which requires a balance between safety factors and material efficiency.
Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations, such as geographical location, climate conditions, and site-specific factors, significantly influence the design and construction of structural steel frameworks. For example, buildings subjected to high winds or seismic activity necessitate additional reinforcement in their designs. Corrosion protection measures may also be essential in moist or corrosive environments to ensure longevity. Understanding these factors not only enhances safety but also optimizes material usage, leading to more sustainable practices in construction.
Aesthetic Integrations
Beyond functionality, architectural aesthetics play a vital role in structural steel construction. Designers can utilize various steel shapes, finishes, and colors to unify form and function elegantly. Exposed steel beams and columns can become striking design elements that enhance architectural appeal, offering minimalistic and industrial looks that resonate with contemporary architecture. Various connections and layouts can create distinctive visual patterns, allowing a structure to command visual impact within its surroundings.
Innovative Techniques in Structural Steel Construction
Prefabrication and Modular Construction
Innovations in construction methods, particularly prefabrication and modular construction, are transforming how structural steel buildings are developed. Prefabrication involves manufacturing steel components off-site under controlled conditions, ensuring precision and quality before transportation to the construction site for assembly. Modular construction takes this a step further by creating entire sections of a building as modules, which are then assembled on-site. This method significantly reduces construction time and enhances site safety through reduced exposure to hazards. Additionally, it allows for better cost management as the construction schedule can be more strictly controlled and aligned with project delivery timelines.
Sustainable Practices
With the growing emphasis on sustainability, the structural steel construction industry is adopting eco-friendly practices. These include sourcing recycled steel, optimizing designs to reduce waste, and implementing energy-efficient processes during steel fabrication. Moreover, steel’s inherent properties make it conducive to energy-efficient design principles and practices, such as utilizing natural light and optimizing heating and cooling systems. The concept of “green buildings” integrates steel with various sustainable materials, providing a comprehensive approach that supports environmental stewardship while maintaining structural integrity.
Smart Technologies in Design
The integration of smart technologies and building information modeling (BIM) has revolutionized structural steel construction. BIM facilitates collaborative design and planning, allowing architects, engineers, and construction teams to visualize and coordinate a project in real-time, ultimately reducing errors and miscommunication. Furthermore, the use of sensors in steel structures can monitor real-time data regarding structural health, providing insights into maintenance needs and ensuring the longevity of buildings.
Challenges in Structural Steel Construction
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating regulatory compliance can be one of the more challenging aspects of structural steel construction. Various codes and standards govern the materials, design, and execution processes that must be adhered to, which can vary significantly by region. Builders must maintain current knowledge of these regulations to avoid penalties and ensure safety. Regular training and engaging with legal and regulatory experts can help in maintaining compliance and following best practices effectively.
Cost Management Strategies
Cost management remains a critical challenge in the structural steel construction sector, influenced by fluctuating prices of raw materials and labor. Implementing effective cost management strategies necessitates early budgeting, accurate forecasting of expenses, and efficient procurement processes. Identifying alternative materials or methods, employing lean construction principles, and utilizing technology for efficient project management can contribute to cost savings throughout the project lifecycle.
Labor Shortages and Skills Development
The structural steel construction industry faces a significant challenge with labor shortages and the need for skilled workers. As the construction sector grows, the demand for qualified labor outpaces the supply, resulting in project delays and increased costs. Addressing this issue requires investment in workforce development programs focused on apprenticeship and training initiatives, creating pathways for new workers into the industry. Collaborations with educational institutions can promote awareness and interest in careers related to structural steel construction, ensuring a future-ready workforce.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Construction
Advancements in Material Science
Future trends in structural steel construction are being greatly influenced by advancements in material science. Research continues to explore new steel alloys and treatments that enhance strength, ductility, and sustainability. Materials such as high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel provide superior performance while minimizing material usage. Innovations related to corrosion resistance also offer the possibility of longer-lasting structures, encouraging more sustainable practices within the industry.
Integration of Digital Tools
The shift towards digitalization is reshaping every aspect of structural steel construction, from design to execution. Digital tools such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are enhancing visualization and collaboration among project stakeholders. These technologies not only facilitate better planning but also improve site safety by allowing workers to visualize how the components fit together before physical assembly, leading to fewer errors and enhanced productivity.
Global Market Insights
The global market for structural steel construction is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by urbanization, infrastructural development, and increasing government investments. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Africa, present opportunities for expansion as the demand for residential and commercial buildings escalates. Companies must remain agile and responsive to market dynamics, adapting their strategies to capture growth opportunities while addressing challenges related to sustainability and labor shortages.
FAQs:
What is structural steel construction?
Structural steel construction is a method of building using steel framing to create structures like bridges, buildings, and towers.
What are the benefits of structural steel construction?
Benefits include durability, flexibility in design, cost-effectiveness, and ease of assembly, making it a popular choice for large projects.
How does environmental impact affect structural steel construction?
Considerations include sourcing materials responsibly, reducing waste, and ensuring energy efficiency in design and construction practices.
What innovations are shaping the future of structural steel construction?
Innovations include the use of prefabrication, smart technologies, and advancements in material science to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
What challenges does the structural steel construction industry face?
Challenges include regulatory compliance, fluctuating material costs, and a shortage of skilled labor in the construction workforce.